Vietnam is a Southeast Asian country renowned for its stunning natural landscapes, diverse cuisine, rich culture, and affordable prices. In recent years, Vietnam has become a popular destination for tourists from all over the world. In this post, we’ll provide you with essential travel information about Vietnam, covering geography, climate, visas, transportation, destinations, food, and suggested itineraries.
Topography and climate
Based on geography and climate, Vietnam is divided into eight regions: Northwest, Northeast, Red River Delta, North Central Coast, South Central Coast, Central Highlands, Southeast, and Mekong River Delta. Each region has relatively different climatic and topographic characteristics.
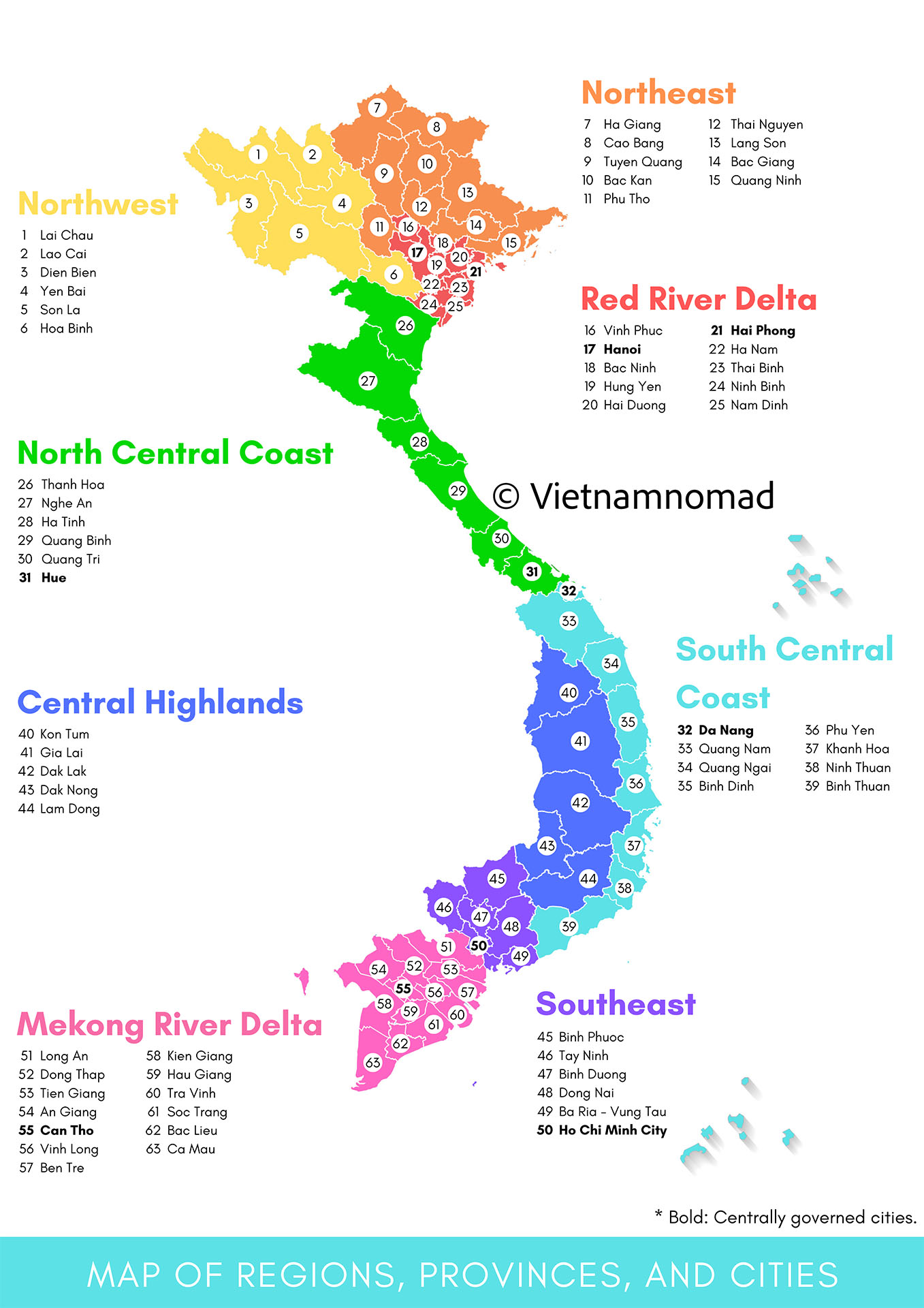
1. Northwest
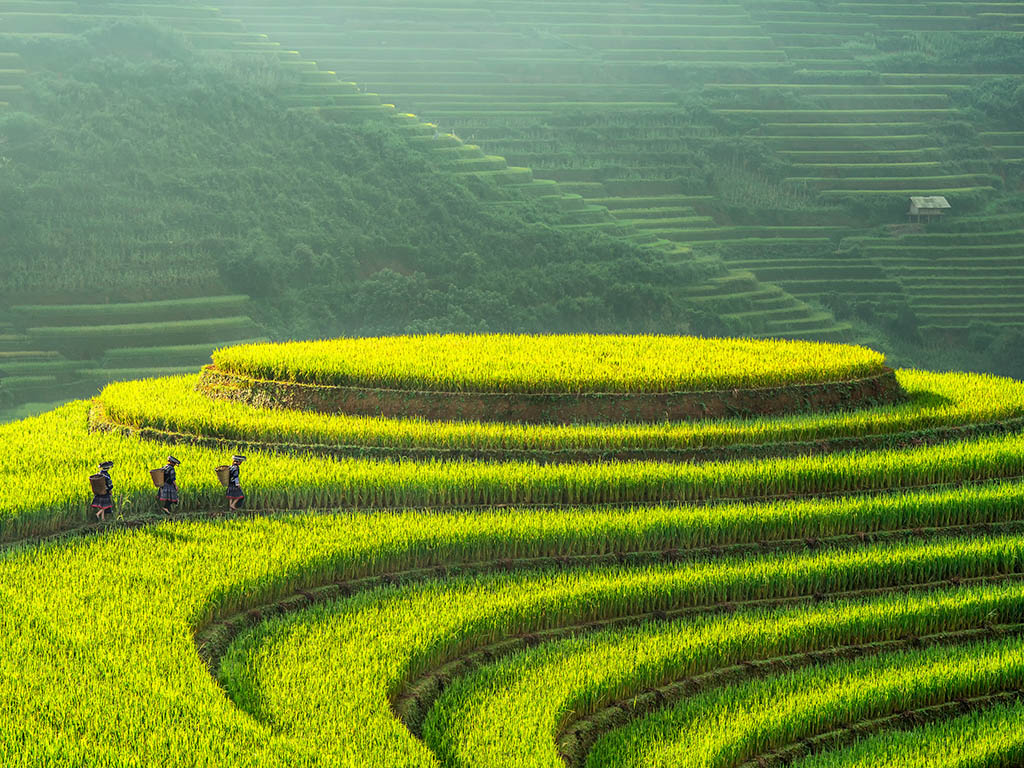

Northwest Vietnam consists of 6 provinces: Dien Bien, Son La, Hoa Binh, Yen Bai, Lai Chau, Lao Cai. The famous tourist destinations: Sapa (Lao Cai), Mu Cang Chai (Yen Bai), Dien Bien Phu (Dien Bien), Mai Chau (Hoa Binh), Moc Chau (Son La). It is a mountainous area which shares the borderline with China and Laos. This is home of magnificent fold mountains and extremely unmatched landscapes.
The region has two distinct seasons: summer and winter. The summer (April to October) is hot and humid. Winter (November to March) is cold, cloudy that is characterized by drizzle. The average annual temperature is about 25 ºC. In winter, the lowest temperature is in December and January; some places have temperatures below 0 ºC.
2. Northeast
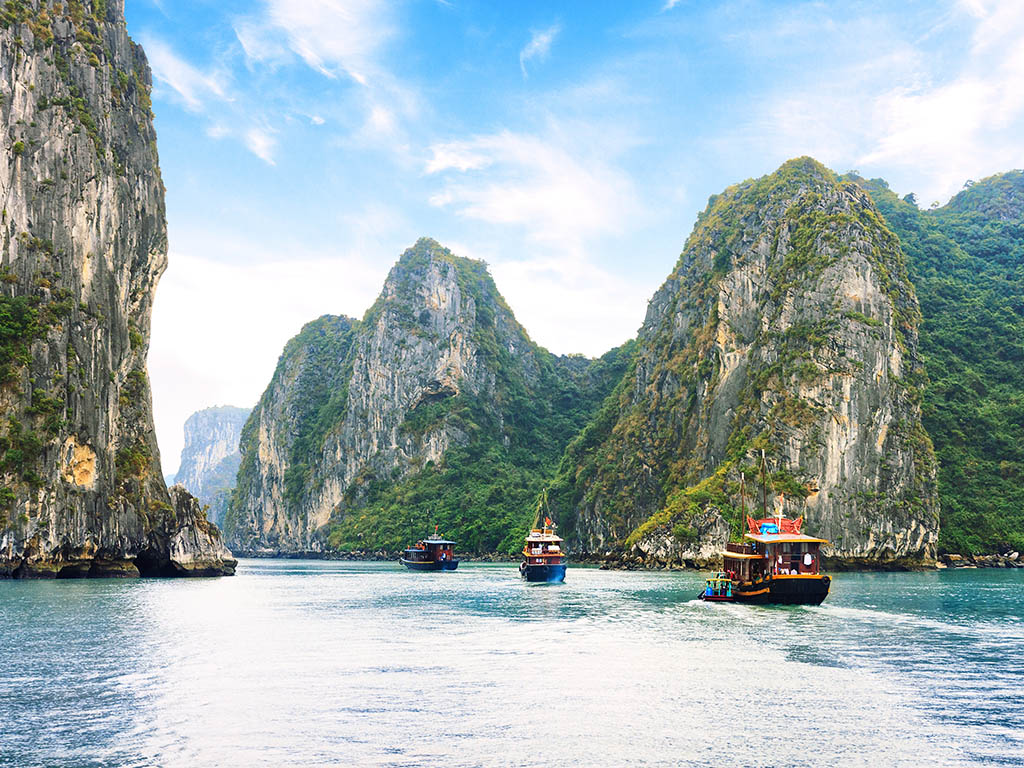

Northeast Vietnam consists of 9 provinces: Ha Giang, Bac Giang, Bac Kan, Cao Bang, Lang Son, Phu Tho, Thai Nguyen, Tuyen Quang, Quang Ninh. The famous tourist destinations: Dong Van (Ha Giang), Ban Gioc Waterfall (Cao Bang), Ba Be Lake (Bac Kan), Ha Long Bay (Quang Ninh), Mau Son (Lang Son). The region is geographically distinguished with the Northeast by the Red River. There are middle-high mountain ranges blended with vast plateaus. The complicated system of water bodies carving into the limestone mountains creating deep valleys across the region.
The climate is quite similar to the Northwest, but the region is more affected by the humid monsoon climate than the Northwest. Therefore, the Northeast is directly affected by tropical storms in the summer.
3. Red River Delta
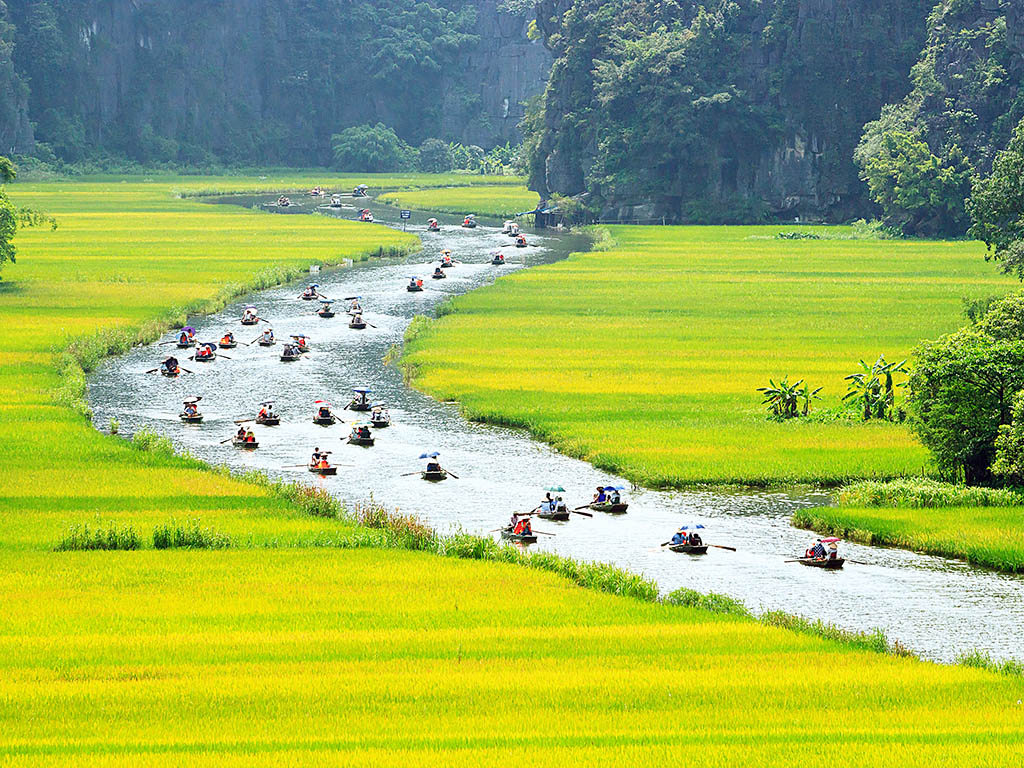

The Red River Delta consists of 10 provinces: Bac Ninh, Ha Nam, Hanoi, Hai Duong, Hai Phong, Hung Yen, Nam Dinh, Ninh Binh, Thai Binh, and Vinh Phuc. The famous tourist destinations include Hanoi, Cat Ba (Hai Phong), Do Son (Hai Phong), and Trang An (Ninh Binh). The delta is situated in the north of Vietnam and is one of the most densely populated regions in the country due to its fertile soil and a large concentration of waterways, which are advantageous for agricultural activities.
Like the Northeast and Northwest, the Red River Delta also has two distinct seasons: summer from April to November and winter from December to March. However, the weather here is milder than in the other two regions.
4. North Central Coast
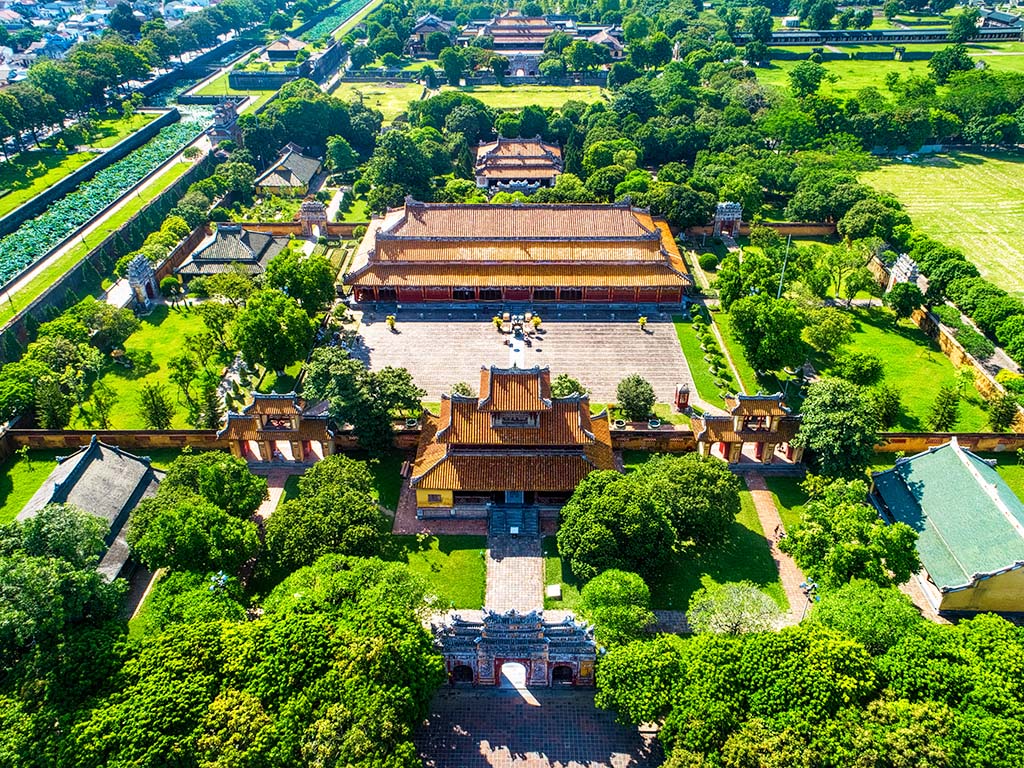

The North Central region consists of 6 provinces: Ha Tinh, Nghe An, Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Thanh Hoa, and Hue. The famous tourist destinations include Thien Cam Beach (Ha Tinh), Cua Lo Beach (Nghe An), Phong Nha – Ke Bang (Quang Binh), and Hue. This region is a long, narrow stretch of land and is one of the most important economic regions, featuring aquaculture and tourism.
Due to the northeast monsoon, the whole area is affected by cold, rainy weather in the winter, which is different from the dry winter weather in the North. In the summer, the southwest monsoon (also known as the Laos wind) brings a hot and dry climate to the region. During this time, the daily temperature can reach over 40ºC, while air humidity is very low.
5. South Central Coast
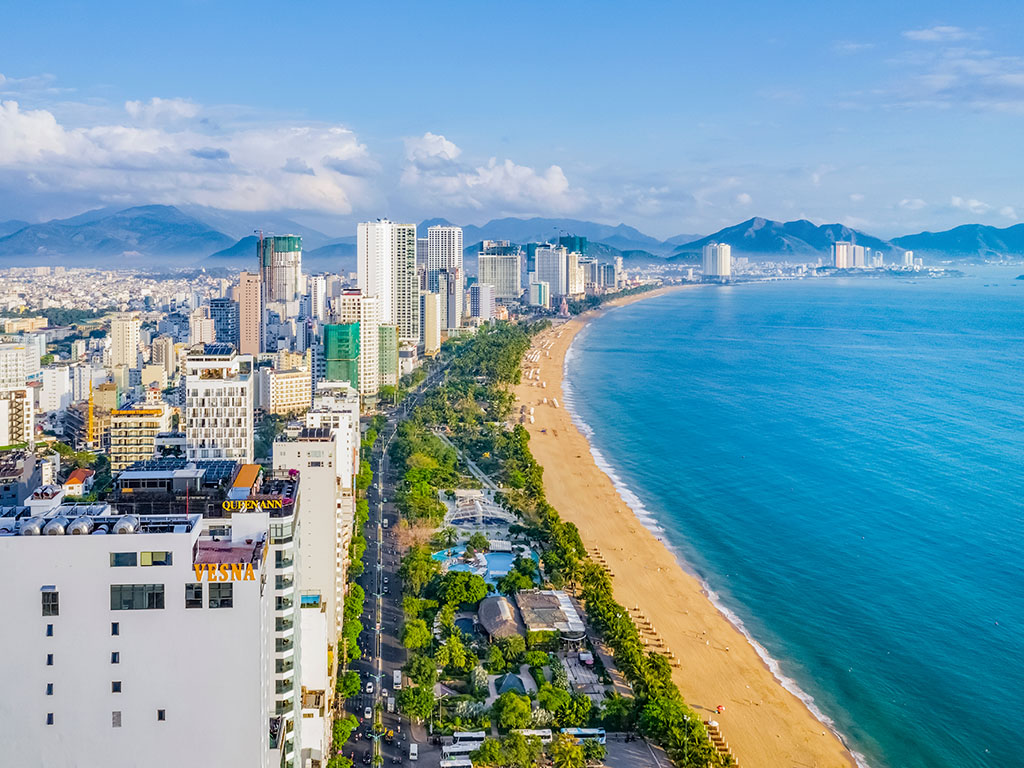

South Central Coast consists of 8 provinces: Da Nang, Quang Nam, Quang Ngai, Binh Dinh, Phu Yen, Khanh Hoa, Ninh Thuan, Binh Thuan. The famous tourist destinations: Da Nang, Hoi An (Quang Nam), Quy Nhon (Binh Dinh), Nha Trang (Khanh Hoa), Mui Ne (Binh Thuan). The terrain is varied, with mountains in the west and narrow coastal plains in the east.
This area has a climate quite similar to the North Central Coast but is drier. Generally, Central Vietnam experiences less rain in the summer and more rain in the winter.
6. Central Highlands
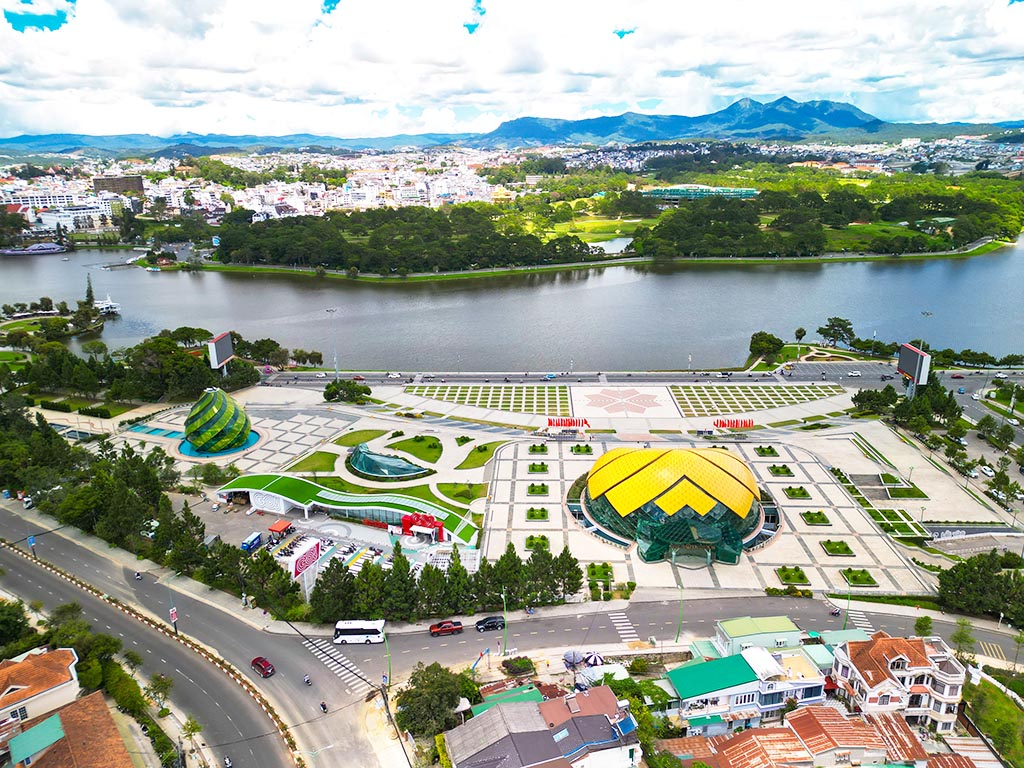

The Central Highlands consists of 5 provinces: Dak Lak, Dak Nong, Gia Lai, Kom Tum, and Lam Dong. The famous tourist destinations include Dalat (Lam Dong), Mang Den (Kom Tum), and Buon Ma Thuot (Dak Lak). The region consists of many plateaus surrounded by mountain ranges. The Central Highlands is known as the coffee capital of Vietnam, as the fertile basalt soil facilitates the growth of this industrial crop.
The climate in the Central Highlands is divided into two seasons: the rainy season from May to the end of October and the dry season from November to April, with March and April being the hottest months. Particularly, the areas over 1,000 meters high have a cool climate all year round.
7. Southeast
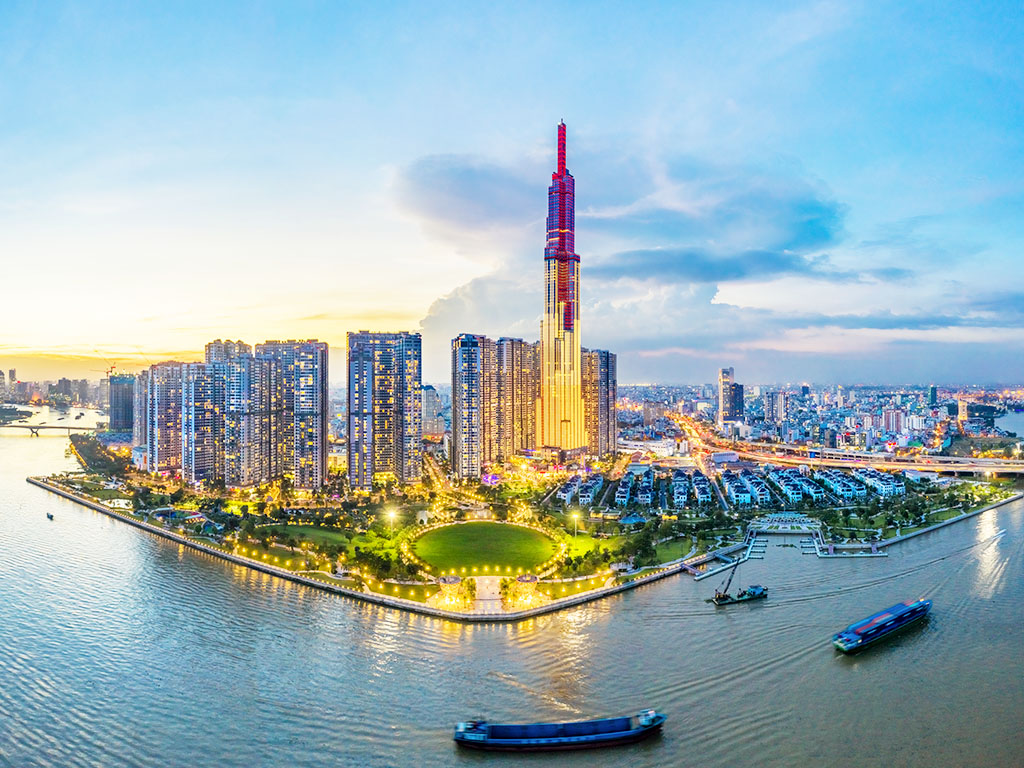

Southeast Vietnam consists of 6 provinces: Ba Ria Vung Tau, Binh Duong, Binh Phuoc, Dong Nai, Tay Ninh, and Ho Chi Minh City. The famous tourist destinations include Ho Chi Minh City, Vung Tau Beach (Ba Ria Vung Tau), Con Dao Island (Ba Ria Vung Tau), and Black Virgin Mountain (Tay Ninh). The Southeast is a highly industrialized zone with vast areas used for industrial trees and factories. The landscape features lowland plains and low mountain ranges, and it is where major river systems converge, focusing on vital ports and tourism.
The region experiences an equatorial tropical climate with abundant sunshine and high humidity. The annual average humidity is about 80 – 82%. There are two distinct seasons: the rainy season from May to November and the dry season from December to April.
8. Mekong River Delta
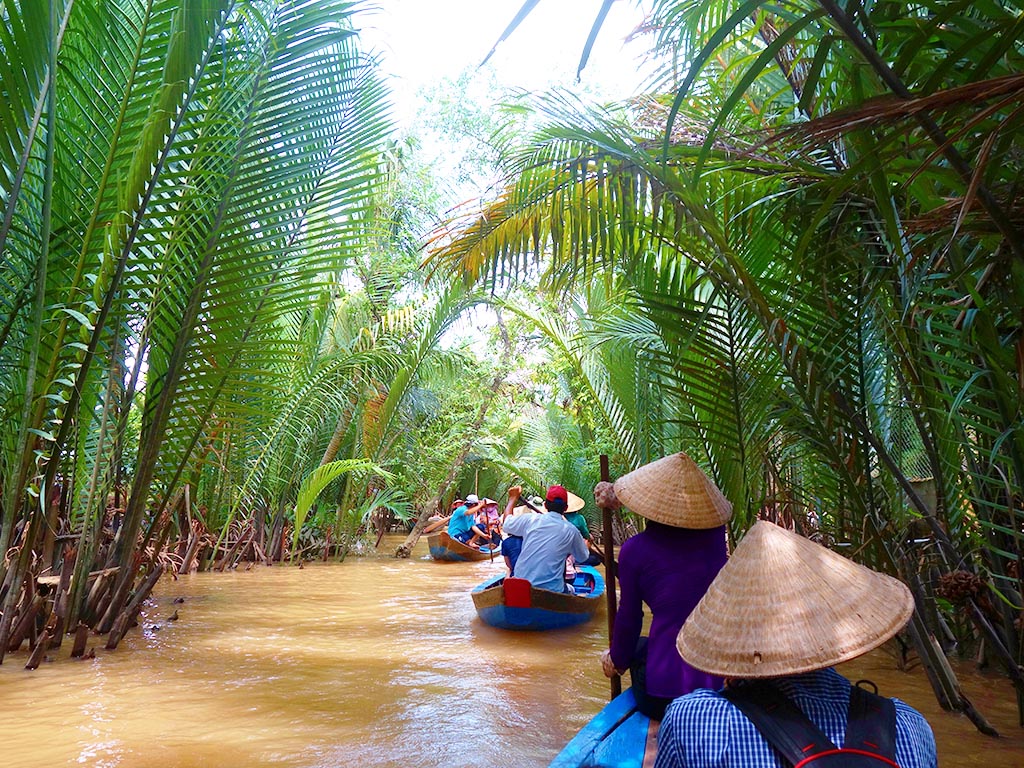

The Mekong River Delta consists of 13 provinces: Long An, Tien Giang, Ben Tre, Vinh Long, Tra Vinh, Hau Giang, Soc Trang, Can Tho, Dong Thap, An Giang, Kien Giang, Bac Lieu, and Ca Mau. The famous tourist destinations include Can Tho, My Tho (Tien Giang), Tram Chim (Dong Thap), Chau Doc (An Giang), and Phu Quoc (Kien Giang). The Mekong Delta is a low-lying region, with some areas below sea level, prone to frequent flooding.
The climate of the Mekong Delta is similar to that of the Southeast: tropical monsoon climate with two distinct seasons – the rainy season (May to November) and the dry season (December to April).
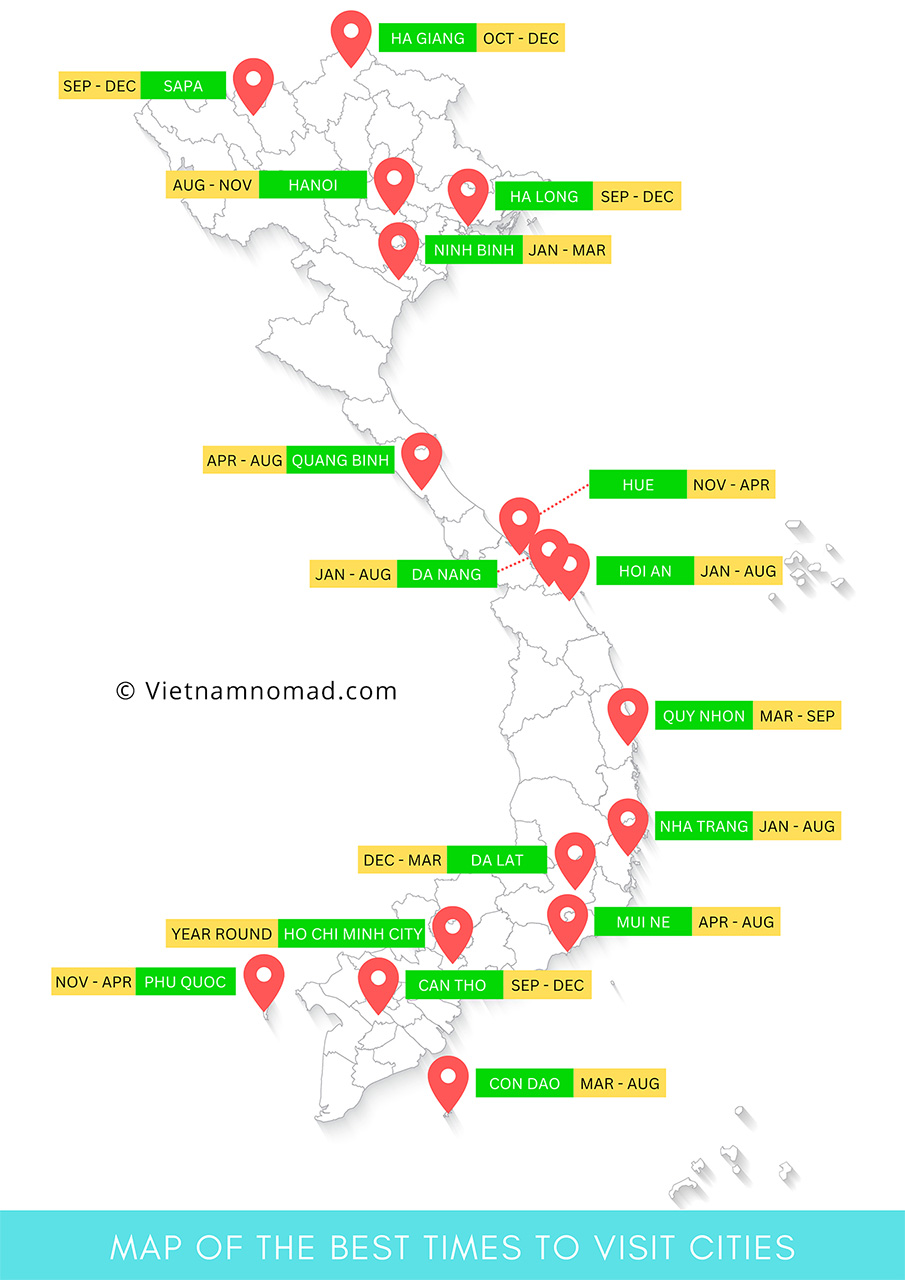
Best time to visit Vietnam
Due to Vietnam’s extensive territory and varied terrain, the climate differs significantly across regions. While the North and South regions experience heavy rains in the summer, the coastal regions receive more rain in the winter. Overall, the best time to explore Vietnam is from December to April, when the weather is cool and dry, also the peak tourist season.
Visas
As of mid-August 2023, Vietnam’s new visa policy extends the stay for visitors from 13 countries with unilateral visa exemption from 15 days to 45 days. Currently, there are 26 countries that enjoy Vietnam’s visa exemption. Here’s a quick overview of countries with exemption periods:
- 14 days: Myanmar, Brunei
- 21 days: The Philippines
- 30 days: Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Cambodia, Laos, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan
- 45 days: Germany, France, Italy, Spain, United Kingdom, Russia, Japan, South Korea, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland, Belarus
- 90 days: Chile, Panama
For those not from visa-exempt countries, obtaining a Vietnam e-visa is easy. Vietnam offers electronic visas to citizens of all countries and territories, allowing a stay of up to 90 days. The e-visa fee is $25 for a single-entry visa and $50 for a multiple-entry visa. Apply at the official website of the Vietnam Immigration Department.
Another option is Vietnam Visa on Arrival, where you will be issued a visa upon arrival at the airport. However, this method is quite traditional and is often suitable for tour group travelers.
Money and exchange
The currency used in Vietnam is the Vietnamese dong, or the ‘dong’. There are 10 common denominations ranging from 500 dong to the highest denomination of 500,000 dong. The current exchange rate is approximately 1 US dollar equals about 25,000 dong, meaning the highest denomination of 500,000 dong is roughly equivalent to 20 US dollars.
Transportation
Vietnam has a relatively well-developed transportation network, including international and domestic airports, the North-South railway, and extensive road networks.
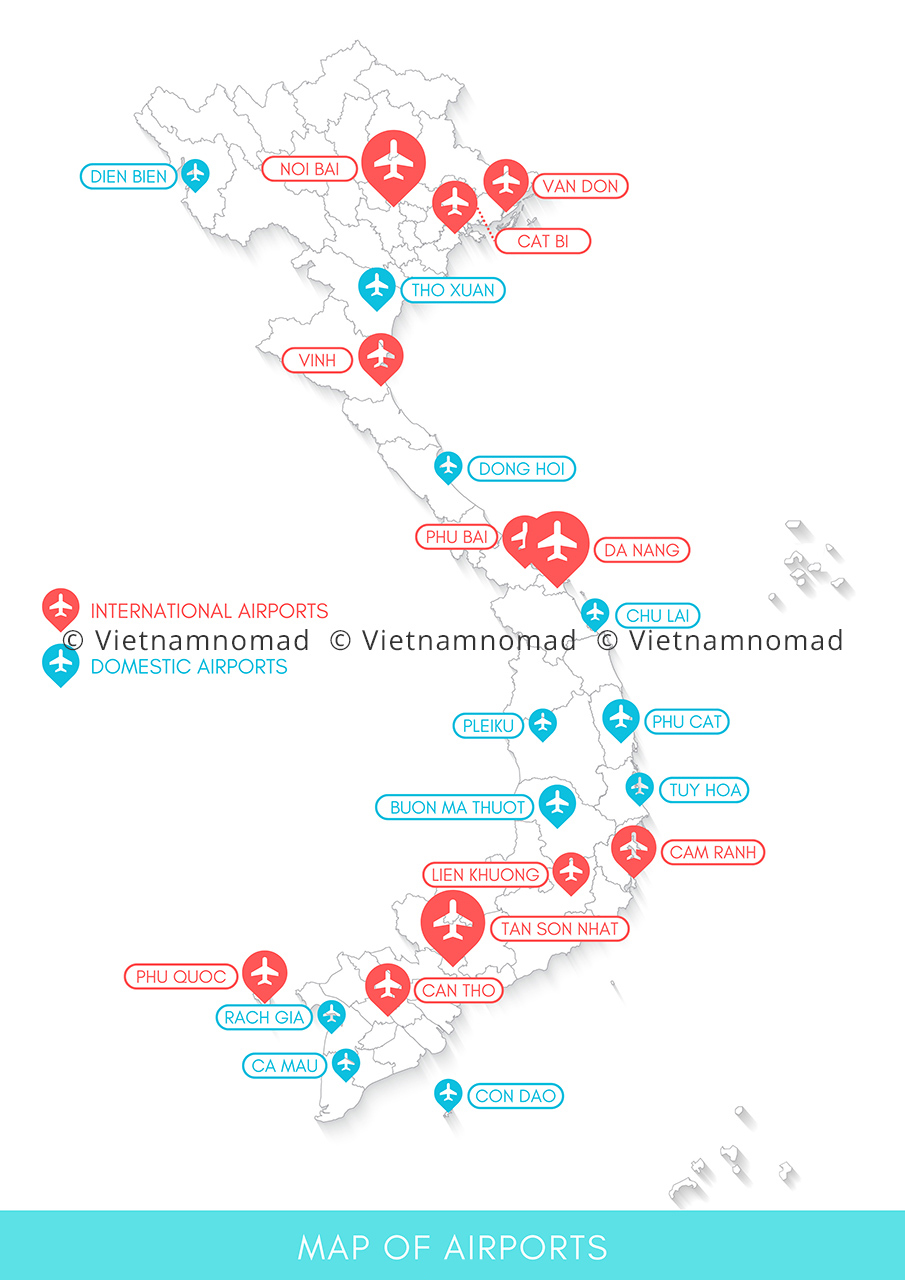
Vietnam has 22 civilian airports, with 11 international airports. The largest are Tan Son Nhat in Ho Chi Minh City, Noi Bai in Hanoi, and Da Nang in Da Nang, serving as major gateways for tourists.
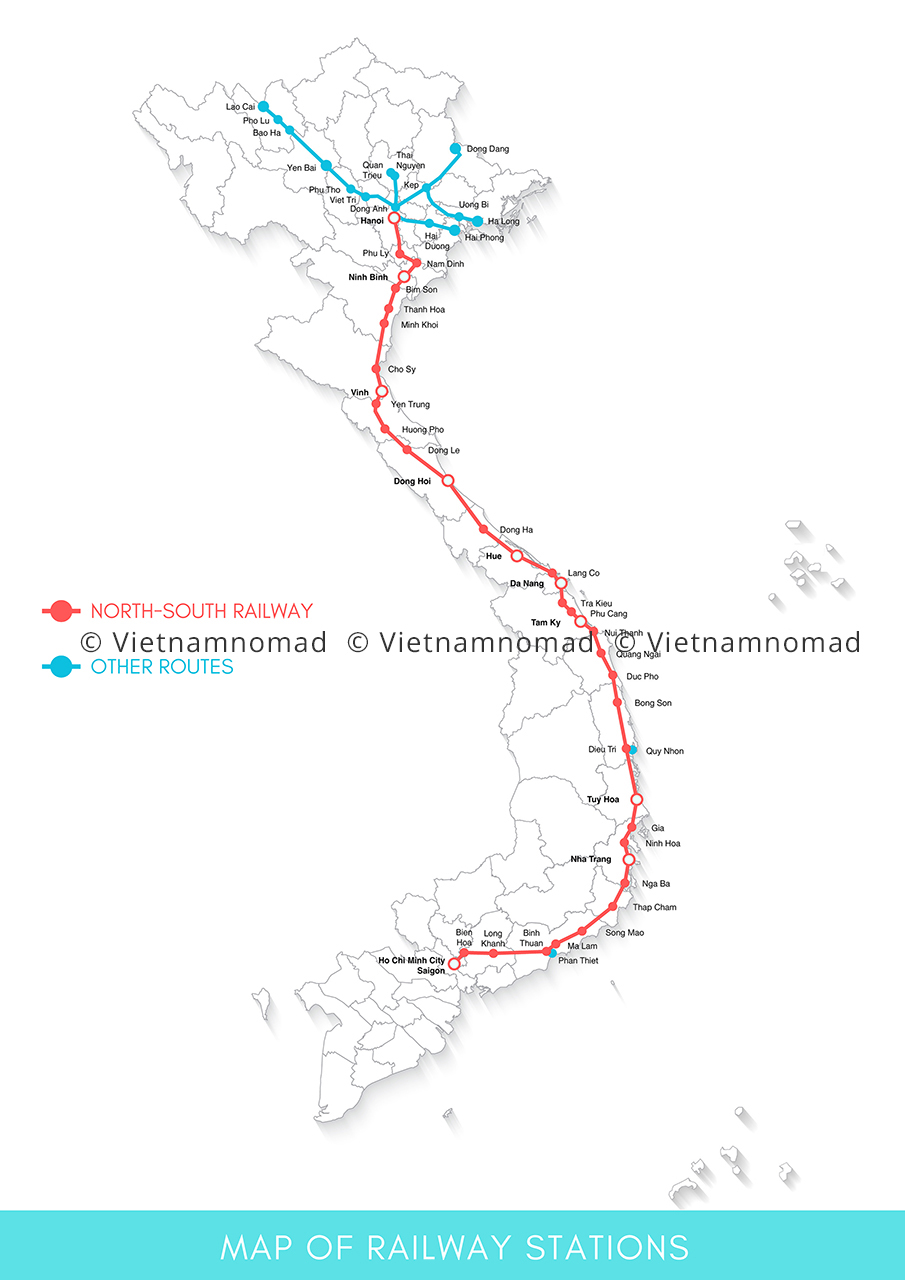
The North-South railway stretches 1,726 kilometers from Hanoi to Ho Chi Minh City. Despite being an aging railway system of nearly 80 years old, traveling by train offers a uniquely captivating experience thanks to the scenic views along the way. One drawback of this railway route is its slow speed, with the journey from Hanoi to Ho Chi Minh City taking approximately 30 hours.
Vietnam’s road network spans provinces, with National Route 1A and the North-South Expressway serving as major arteries. However, numerous roads are narrow and suffer from deterioration, making self-driving not recommended for tourists unfamiliar with Vietnamese roads. For destinations within a 300-kilometer radius, buses offer a convenient and economical transportation option.
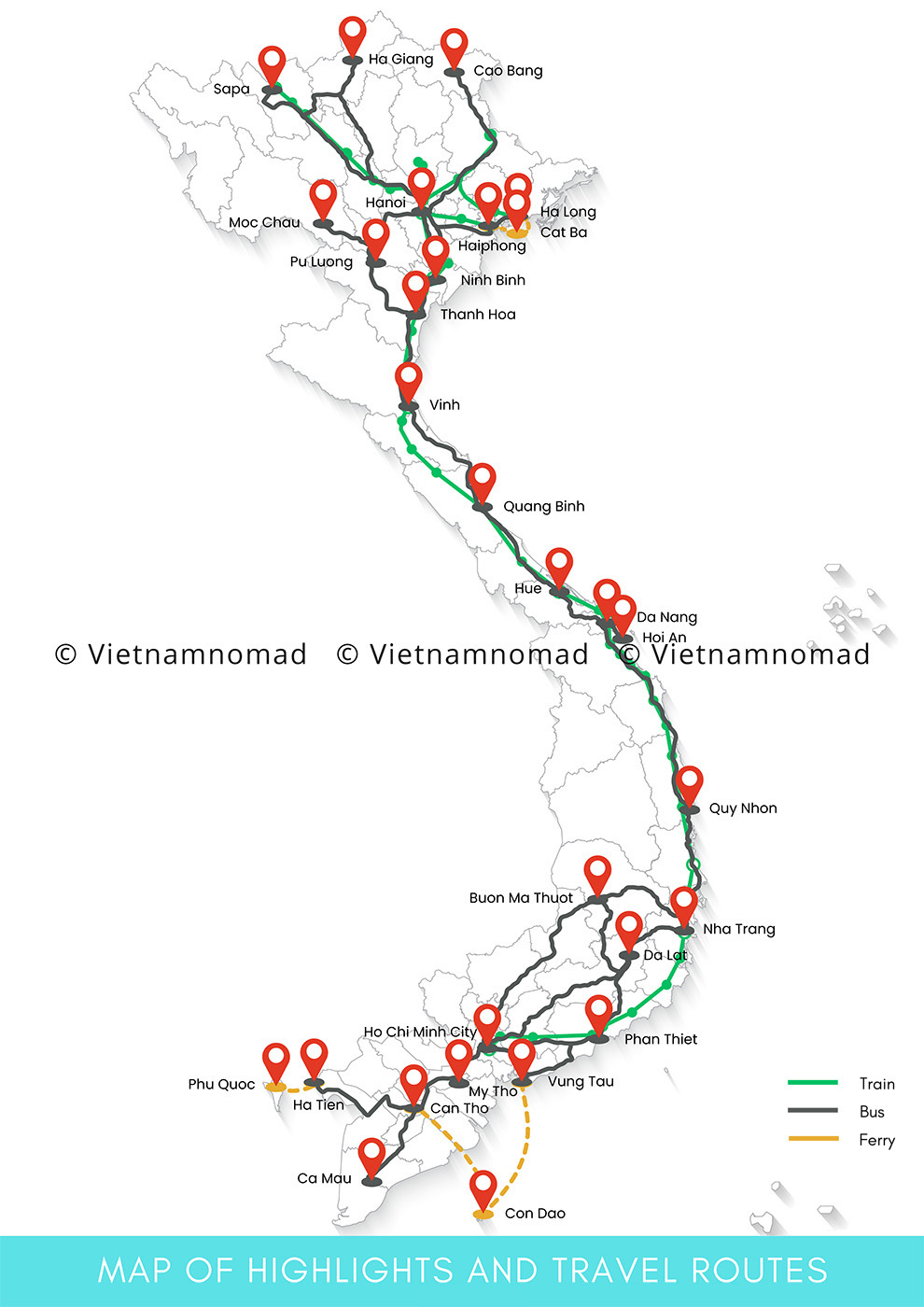
Explore more Vietnam maps >
Internet
In Vietnam, Wi-Fi is everywhere, from restaurants, cafes, and hotels to roadside eateries. Public spots like airports, train stations, or bus terminals also provide free Wi-Fi access. However, if you want to maintain continuous connectivity, you can purchase a SIM during your stay. Standard packages typically cost around $7 per month, offering 4GB of daily internet usage. SIMs are conveniently sold at airports.
Cost of traveling in Vietnam
Traveling in Vietnam is notably affordable. According to a survey conducted in our Welcome to Vietnam community, the average cost for a 3-week trip ranges from 750 to 1,500 US dollars. It’s worth noting that expenses in major cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City tend to be higher compared to other destinations in the country.


